Zigbee and Z-Wave explained
Both Protocols are based on a Mesh network topology, which means that each device also serves as a node in the network allowing signals to jump from one device to another until it reaches it’s destination device. This expands the range almost unlimitedly as well as providing a very stable and solid network. If one device fails, the signal will take another route to the destination.

What Is Zigbee?
Zigbee communication protocol is an open standard protocol used on mesh networks for wireless communication between smart devices. The Zigbee protocol, signals can jump from one Zigbee device to another in an open structure without connecting each device to a central hub (Wifi).
Zigbee uses the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol that solve the high costs and power consumption of smart devices.
The Zigbee protocol supports communication between 65,000+ devices using a 2.4GHz frequency which increases the range and penetration.
What Is Z-Wave?
Z-Wave is a standard protocol used on mesh networks for wireless communication between intelligent devices. Even though Z-Wave is owned by Sigma design, it is maintained by the Z-Wave Alliance, a coalition of 400 companies, which makes it very reliable, also in the future.
This protocol is prevented from being altered by anyone which is the core of the Z-Wave protocol as it assures effective interoperability and security.
The Z-Wave protocol supports up to 232 devices on the 908.2MHz frequency with a communication range between the devices up to about 100 m. These features make Z-Wave an attractive option for Internet of Things (IoT) and home automation.
Both protocols require a Gateway or Bridge to connect, unlike wifi devices that connects through your Internet connection to a cloud-based server. This means that Zigbee and Z-Wave devices often operates even without Internet connection and gives you higher security and control.
Some Home assistants also work like a gateway, but mostly (and recommended to eliminate the need of Internet connection) you would need a dedicated Gateway or Bridge.
 offers several bridges like ZBBridge and ZBBridge Pro, but also the new NSPanel Pro has a build in gateway for Zigbee.
offers several bridges like ZBBridge and ZBBridge Pro, but also the new NSPanel Pro has a build in gateway for Zigbee.
The Aeotec Smart Hub (previously Samsung Smart Hub) is another great gateway as it works with the SmartThings platform that support easy and more complex setups of scenes and routines and supports both Zigbee, Z-Wave and Wifi devices such as IoT devices (vacuum cleaners, locks, TV, etc.) and works with popular home assistants like Google Home, Apple iOS, Ipad iOS and Alexa.
Want to see more? Check out the Zigbee devices on Smart Living Smart Shop
Zigbee versus Z-Wave protocols
1. Reliability
For a mesh network to work correctly, it must use a reliable protocol with very little lost signals caused by interference when other devices use the same frequency.
The Zigbee protocol uses the widely used 2.4GHz frequency in Europe which could result in missing signals because of interference from any other Wifi, microwave, or device running at the same frequency nearby.
The Z-Wave protocol uses the frequency 908.42MHz, but this can also be used by other such as landline telephones. However, the risk of interference on this frequency is much less.
When deciding on which protocol to use, it is important to consider the potential degree of overlapping frequencies which could cause reliability.
2. Interoperability
 The core of IoT is interoperability between devices and their protocols. Interoperability is the ability of devices or computers to communicate and exchange information with other devices. Due to certification differences, interoperability presents a significant difference between the Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols.
The core of IoT is interoperability between devices and their protocols. Interoperability is the ability of devices or computers to communicate and exchange information with other devices. Due to certification differences, interoperability presents a significant difference between the Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols.
Zigbee is maintained by the Zigbee Alliance that consists of 400 member companies responsible for 2500 Zigbee devices and half a billion chipsets. However before, the Zigbee’s certification was not that consistent and some devices whose software did not comply with the Zigbee protocol could receive certification from Zigbee. This encouraged the sale of non-interoperable devices under Zigbee’s name. With Zigbee 3.0, this has changed and all Zigbee 3.0 devices are now unified and interoperable.
Z-Wave is owned by Sigma Designs and maintained by the Z-Wave Alliance who control the certification for Z-Wave devices. From the beginning Z-Wave devices has had interoperability as the certificate ion secures that every certified Z-Wave device works with every Z-Wave controller.
Conclusion: Zigbee products are interoperable with each other only if they were revised before being certified and are version Zigbee 3.0.
Z-Wave products are always interoperable with themselves via the Z-Wave controller.
3. Speed
 Protocol speed is among the first considerations for individuals and organizations when choosing wireless technology. Slow functionality of Smart devices can be annoying, and these two protocols differs in speed.
Protocol speed is among the first considerations for individuals and organizations when choosing wireless technology. Slow functionality of Smart devices can be annoying, and these two protocols differs in speed.
The Zigbee protocol communicates on 915MHz or 2.4GHz frequency. This indicates that the speed of communication with Zigbee is 40-250kbps. This range is fast and supports smart and easy living applications like smart sensors and medical care.
The Z-Wave protocol communicates on 908.42MHz with a speed of 9.6-100kbps, thus significantly slower than Zigbee. This speed range could be suitable in certain IoT uses like smart speakers, butwould be slow for smart sensors and medical care, which need prompt responses.
4. Connectivity
The Zigbee protocol supports mesh networks of + 65.000 devices at the same time. This could be an important factor for large networks like businesses, factories and large offices.
The Z-Wave protocol supports mesh connections with a maximum of only 232 devices, which would mostly be sufficient for home and small businesses.
5. Number of jumps
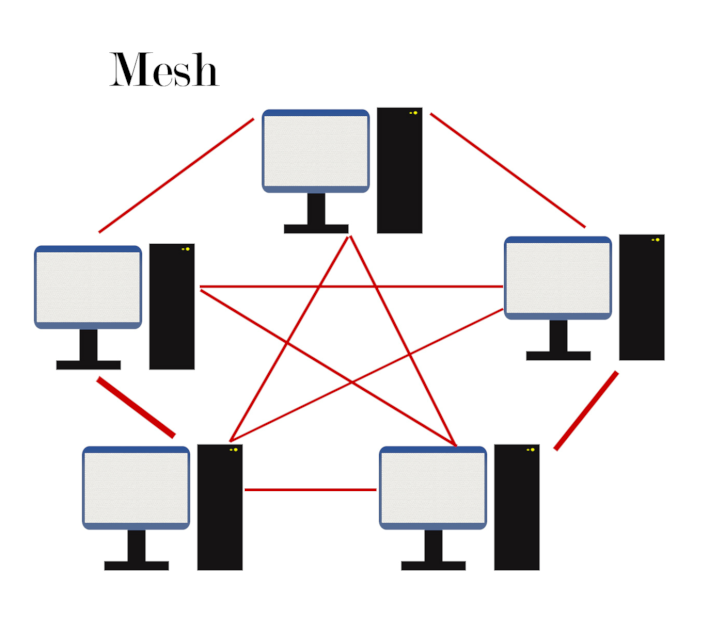 In a mesh network, the devices are interconnected. This implies that signals “jump” between devices instead of going from hubs to devices which can be affected by range.
In a mesh network, the devices are interconnected. This implies that signals “jump” between devices instead of going from hubs to devices which can be affected by range.
The Zigbee protocol supports unlimited number of jumps and therefore supports connections between as many devices as you want.
The Z-Wave protocol supports only four jumps per transmission. This means that signals can only jump between four devices including the destination device.
6. Range of signals
Both protocols have a distance limitation between the devices. If the maximum distance between devices is exceeded the signals will not be transmitted.
The Zigbee protocol provides a strong connection when devices are within 12 meters from each other (indoor). However, due to the high frequency of Zigbee, materials used in walls and indoor equipment can reduce the traveling distance of the signal.
Zigbee supports faster speed, more jumps, and more connections, but the distance between devices must be kept below 12 meters.
The Z-Wave protocol offers a strong connection up to a distance of 100 meters between devices (indoor). As the Z-Wave protocol uses a low frequency, transmission through walls and other obstructions is stronger and may be one of the considerable factors when choosing the protocol, despite the limited number of jumps and low speed of the Z-Wave protocol.
7. Security
 Security is another criterion for the network topology. Here, security would mean, that the transmissions can’t be hacked or changed. There are a number of devices that requires high security like medical equipment, locks, alarms and transmission of data.
Security is another criterion for the network topology. Here, security would mean, that the transmissions can’t be hacked or changed. There are a number of devices that requires high security like medical equipment, locks, alarms and transmission of data.
Both protocols use the AES128 standard for encryption and is a mandatory requirement for certification. AES128 is a trusted security standard that online banks and government agencies use.
The Z-Wave protocol has an extra layer of security. Security 2 (S2) layer is also tagged as mandatory for every device that needs Z-Wave certification. This layer protects smart devices from being used in a DDOS attack.
This additional security does not necessarily make Zigbee less secure because it also uses AES128 symmetric encryption.
8. Power usage
 Some smart devices require optimal battery power, while others require very little. In both scenarios, the signal communication should have minimal effect on battery life; that is, it should use low power. This is very critical while using sensitive devices like smart locks and sensors.
Some smart devices require optimal battery power, while others require very little. In both scenarios, the signal communication should have minimal effect on battery life; that is, it should use low power. This is very critical while using sensitive devices like smart locks and sensors.
Both protocols use low power, but the Zigbee protocol is better for using less energy than the Z-Wave protocol. Zigbee protocol was built on the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol standard. Amongst other advantages, this protocol standard gives Zigbee an edge in minimizing power usage in smart devices and allow many devices to run on batteries that last 1-2 years, thus less cables in your installation.
New Z-Wave devices are trying to close this gap by using less power than the former offerings, but Zigbee devices still has less power usage and better battery performance.
9. Price
Zigbee products are in general less expensive than Z-Wave devices, mainly because of the use of IEEE 802.15.4 protocol standard. The price difference between both protocols is not that much, so choosing the best option should first depend on the protocol’s other features.
10. Open and closed standard
Another significant difference between Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols is the network standard.
Zigbee uses open network standards. This form of network is also called an open-source network.
The advantage of Zigbee’s open-source network is that anyone can check the code. This is also a downside as anybody can alter the code to suit their needs. Z-Wave uses closed network standards. In this standard, the code that overrides transmission operations is not made public and cannot be altered.
Z-Wave’s closed standard provides additional security. Every device connected to your hub has a unique ID for easy identification. This adds security to the secure network and ensures interoperability with only Z-Wave devices.
Applications of Zigbee and Z-Wave in IoT
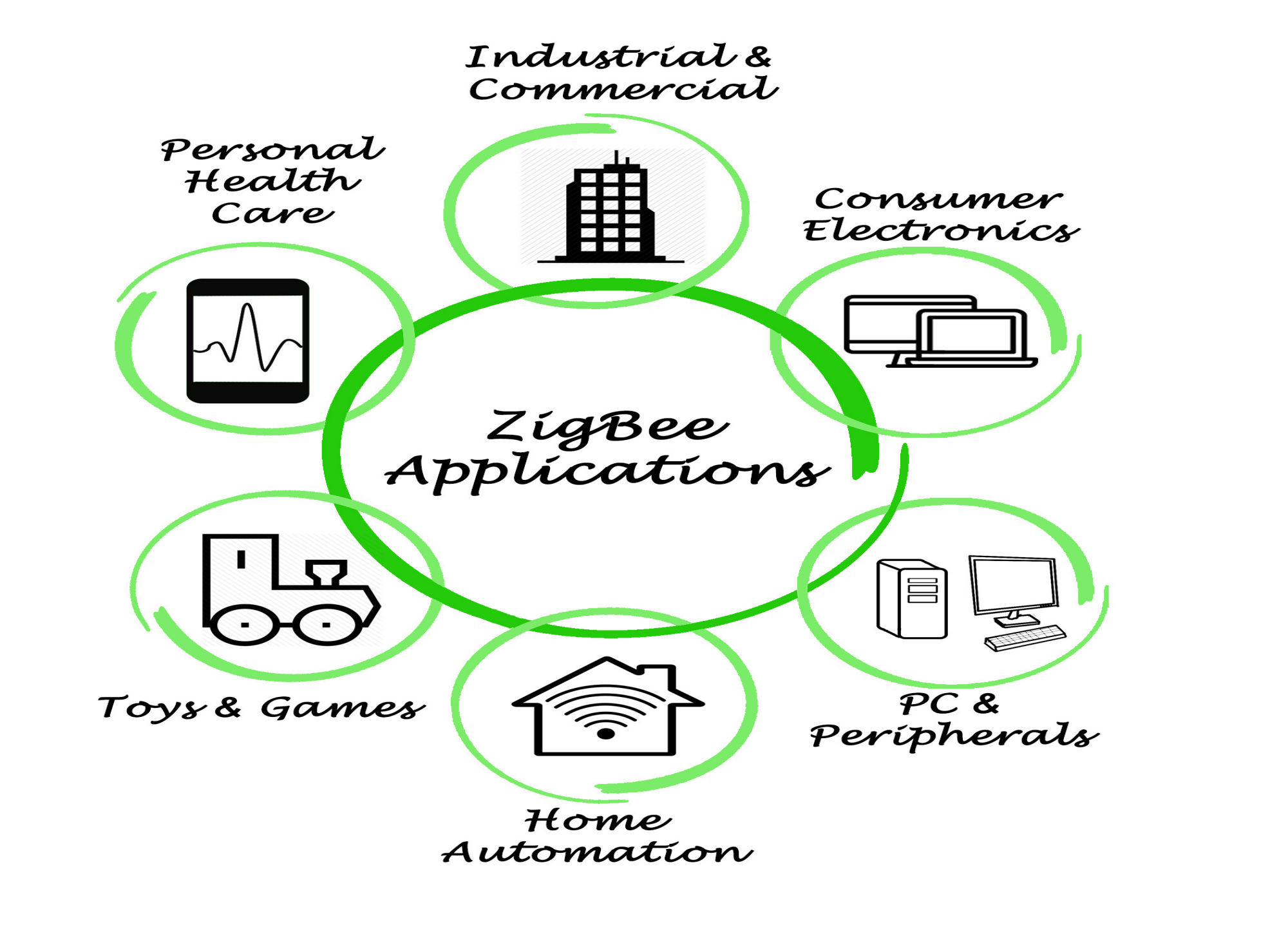 The applications of Zigbee and Z-Wave communication protocols in the IoT era are numerous. Both protocols are excellent options in some applications, but in others, one protocol can have the edge over the other.
The applications of Zigbee and Z-Wave communication protocols in the IoT era are numerous. Both protocols are excellent options in some applications, but in others, one protocol can have the edge over the other.
Home automation is rapidly becoming a norm and is now a typical application of Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols.
The IEEE 802.15.4 standard makes the Zigbee protocol easy to use, supporting robust connections, low cost, and low power usage.
Remote control and management is another primary application of the Z-Wave and Zigbee protocols for controlling IoT devices i like smart locks, smart thermostats, smart lighting, smart plugs, and smart sensors.
Want to see more? Check out the Zigbee devices on Smart Living Smart Shop




